OpenDRT : a nice (experimental) alternative to ACES
An open-source alternative to convert scene-linear data to SDR or HDR display image.
With the Academy Color Encoding System (ACES) becoming omnipresent more and more, it would be worth keeping in mind that it’s not the only solution to have a good color-managed pipeline (let’s keep that for a future article) . I’m not going to try to go too far and stick to the title even tho there is a lot to discuss on the topic.
If most people get into ACES, it’s mainly for its “filmic” looks (provided by the RRT), rather than having a full color-managed workflow. And that is understandable, as individual artists, you most of the time, only care about having the prettiest image possible at the end.
So what if you got a well-formed and pleasing image at the end without having to go through the complexity of ACES ?
Who’s this for ?
My post mainly targets the VFX-CGI audience but OpenDRT work on any open-domain/scene-referred data, including photography and cinematography. (as long as the data is not in a closed-display-domain).
This means that for CGI, you are familiar with a “scene-linear workflow” :
Render -[EXR]> compositing/postprod(linear) -> display-refered final output [jpg,...]
Then the OpenDRT implementation is only available as a Nuke Gizmo and
through Davinci Resolve DCTL feature (on paid licenses) which imply you
are using one of these dccs.
No OCIO support, this means you will have with your traditional workflow in
your rendering DCC and only be able to preview the final image in your
post-prod one which is not an ideal one.
With all of that , this mean my post is aimed at individual artist doing personal projects that would like a quick solution for proper SDR-HDR export. (OpenDRT is probably aimed at additionals goal)
~
First, please have a look at the above repository, read Jed’s explanations and the tool’s documentation.
Before diving into the setup I think it’s important to remind the target of OpenDRT:
The tool has for goal the faithful conversion of open-domain / scene-referred data to a closed-domain : the display. This mean no creative transformations are applied. As such the output’s result can look very neutral and should be graded.
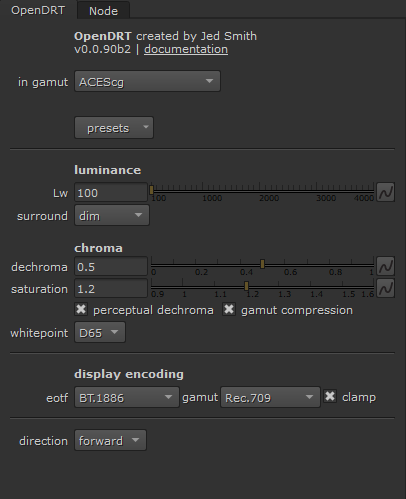
Node knobs
As the tool is constantly changing, Jed’s documentation is not up to date, and thus this post will also probably be.
First thing, tell the tool in which gamut your input is.
I assume the input should be Linearly encoded.
You then have a bunch of presets that will tweak the knobs for you based on your target display encoding.
Lw : this is the nits level of the target display and shouldn’t be
used as a creative adjustment.
- 100nits is the value defined as per the ITU-R BT.2035 specifications and should represent the peak-white value of a display in a dim surround.
surround : the luminance level of the viewing environment.
dark: theatrical viewing environment.dim: “home theater” (low light condition).average: desktop/office average surround.
dechroma : this one is more “subjective”, allowing to control
the amount of chrominance compression that should be applied on values
reaching display maximum (R,G,B=1.0). If HDR imagery needs to be
produced, this can be lowered (as the target domain (hdr) has more
volume to express chroma)
saturation : Expand chroma on the bottom values after the compression by
the dechroma.
See more here .
whitepoint : (from doc) Sets the creative whitepoint. This allows
you to creatively set the whitepoint of your display rendering if
you want it to be different than the technical whitepoint of your
display device. For example, if you set this to D55, neutral colors will
be rendered as a warmer hue compared to the default D65.
display encoding : This part will be re-addressed under.
The
eotfshould correspond to the transfer-function used by the targeted display.
BT.1886 , the default value, correspond to a 2.4 power function, which is the standard for Rec.709.
For the average of user display you should usesRGB Display.
The
gamutcorrespond once again to the gamut that the targeted display is calibrated to. (reminder that sRGB use the same gamut as Rec.709)
.
To adjust these settings properly you have to know the targeted display + user :
The issue is that with today range of displays, this is a rather difficult one to average (until you have the full-control on the display the image is going to be viewed on )
In the case of web publishing, for example, the average user will probably
have a SDR display, sRGB encoded, with an average white peak of 100 nits and
used in an office environment that can be brighter than a dim surround.
If we add smartphones to the equation, thing will get messy …
I’m still digging on the subject trying to gather more info and as such will
close this topic.
So for now, using the presets is, I think a good practice.
Nuke
(For now i’m only going to show how you can use it in Nuke as I don’t have a Resolve License)
- Download the .nk file (Right click on the page > save as > save it somewhere)
- Import the .nk file: File > Insert Comp Nodes
Or alternatively :
- Open the .nk
file and copy all of his content
(ctrl+a, ctrl+c) - Paste in Nuke
(ctrl+v)
Alright, you now have the OpenDRT node.
Node Setup
Things will now get a bit complicated at first. The issue is that has the OpenDRT handle the scene -> display conversion, this will collide with Nuke that try to do the same in the view-transform.
I found 4 different solutions that achieve the same result. I think the last one is recommend to use but it’s good to have other example that might help to understand how everything works.
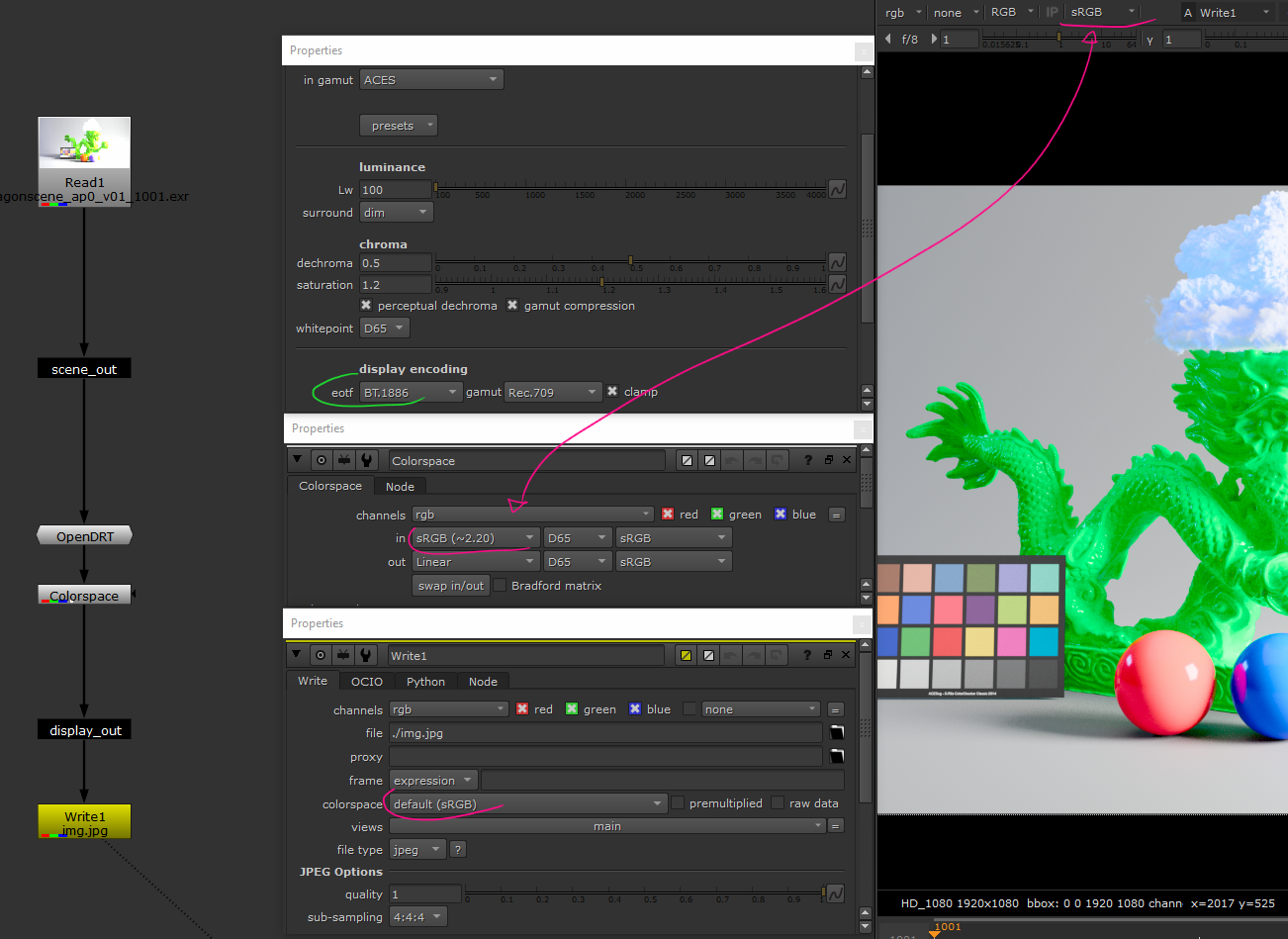
Revert Display
We let the DRT handle everything (with display-encoding), then we apply the invert transform that applied by Nuke:
Writing the data is as before. You just have to be sure that the Colorspace
node has the same in parameters as the colorspace one on the write node.
Nuke Display-encoding disable
We disable Nuke’s handling of the display-encoding. The DRT is the last step.
This means the Nuke view-transform is always off which can be incovenient when you need to preview a node upstream.
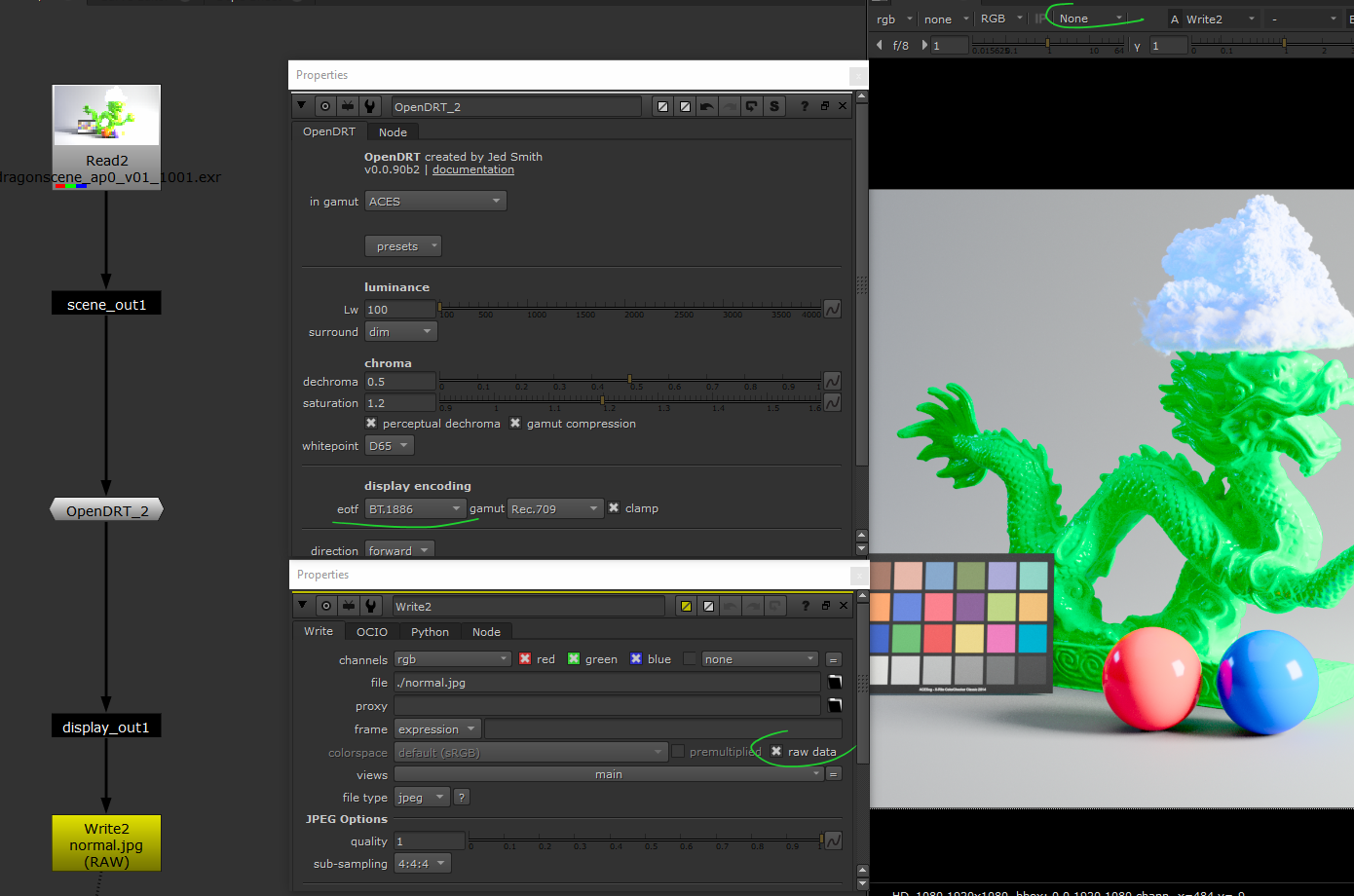
OpenDRT no Display-encoding
One good solution: the OpenDRT doesn’t handle the display encoding but output closed-domain data ready for the display. Nuke apply the display-encoding as usually, writing data is the regular workflow.
Be careful as OpenDRT still handle the gamut conversion from the input to the output. Write node colorspace need to be choosen with this is mind.
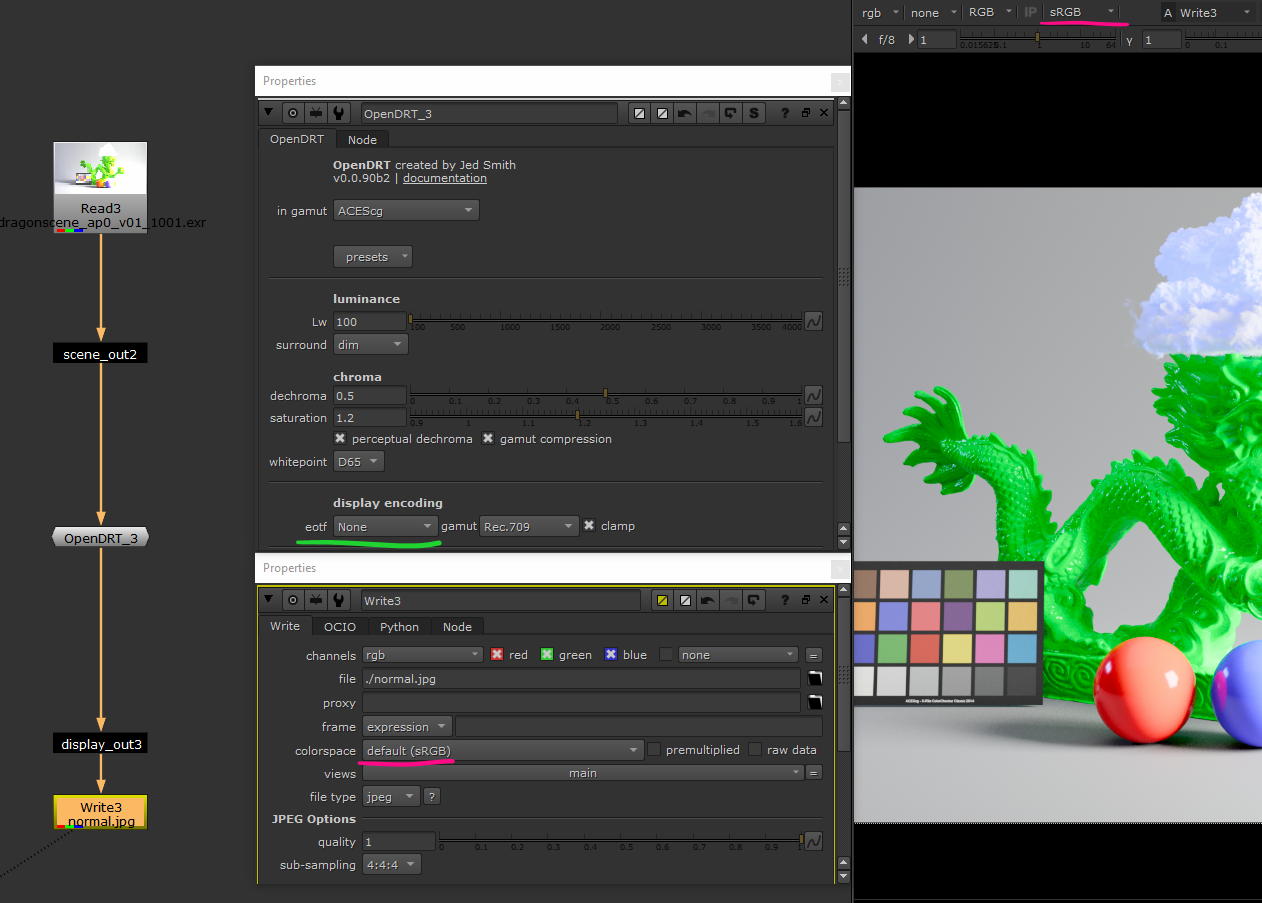
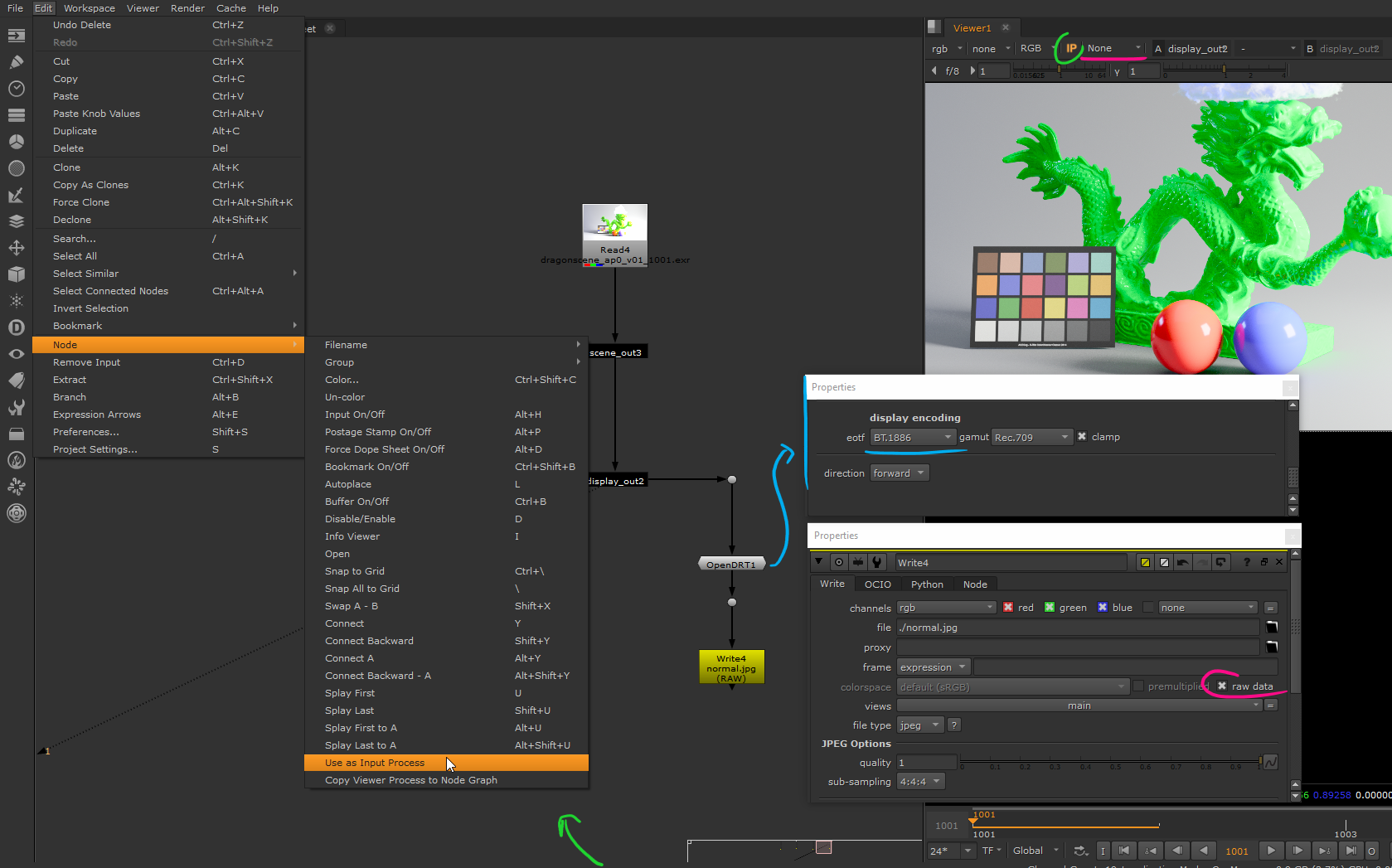
OpenDRT with Viewer Input Process (recommended)
This is probably the best solution :
OpenDRT handle everything, we disable Nuke view-transform but we will be
using its input process feature.
This will allow to always have the OpenDRT active no matter what node we are
previewing (this can be inconvenient when viewing scalar data like
alpha, think to disable the input-process in that case.)
We don’t actually need the node used as input-process to be connected to anything but here I’m making sure it’s connected before the write node, so OpenDRT get baked in at export.
As OpenDRT handled the display encoding we can turn it off on the write node
by checking raw data.
Conclusion
If you tried to compare the result to an ACES processed image you would have probably notice that the image-formation produce much more “excepted” result, among others, in strong colored highlights, which make OpenDRT a solid candidate at better image-formation and a peak of what could be used in the future.
Even if it’s current form kind of break the purpose of a consistant color-managed system across DCCs, it is a nice solution for individuals and looks very promising. (Jed told me it could be actually pretty simple to create an OCIO config so we can only hope he finds time to !).
Make sure to star Jed’s repository on Github !